연결 리스트
∙ 리스트
- 순서를 가진 데이터의 모임, 목록
- TO DO 리스트, 요일...
- 리스트의 주요 연산
> 원소의 참조, 삽입(insert), 삭제(remove), 검색(search)
- 대표적인 리스트 구현 방법
| 배열 | 연결리스트 | |
| 저장공간 | 연속적인 메모리 공간 | 임의의 메모리 공간 |
| 원소의 삽입 & 삭제 | 비효율적 | 효율적 |
| 구현 | 쉬움 | 어려움 |
∙ 연결 리스트
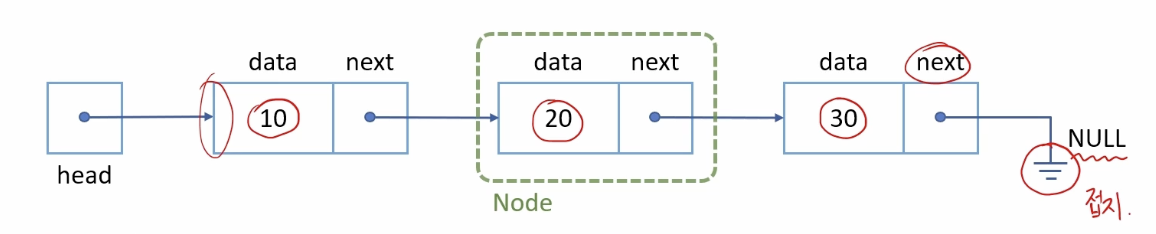
- 데이터와 링크로 구성된 노드(node)가 연결되어 있는 자료 구조
> 데이터(data) : 정수, 문자열, 복합 자료형 등
> 링크(link, next) : 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
> 노드(node) : 데이터와 링크로 이루어진 연결 리스트 구성단위
∙ 연결 리스트 맨 앞에 노드 삽입하기
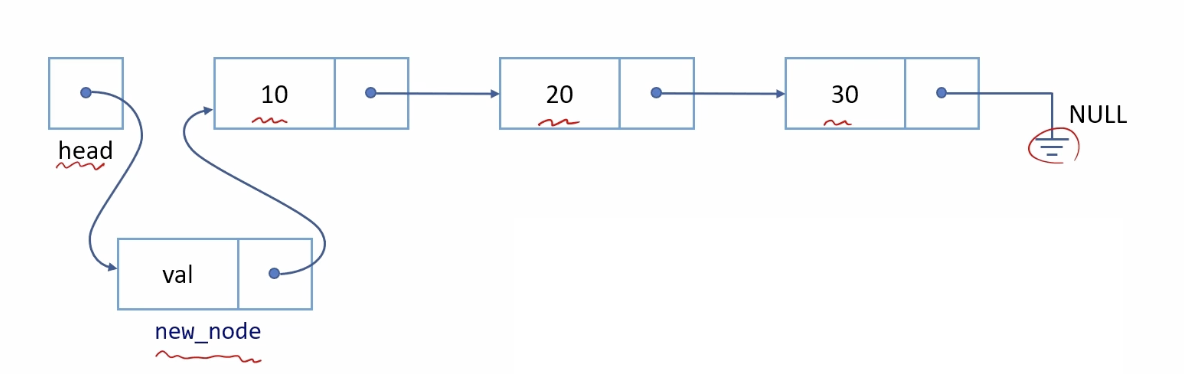
void push_front(int val)
{
Node* new_node = new Node{val, NULL};
if (head != NULL)
new_node -> next = head;
head = new_node;
}head가 가리키게 NULL 값이 아니면 new_node를 가리키게 하고, new_node는 head가 가리키고 있던 값을 가리킨다.
∙ 연결 리스트 맨 앞 노드 삭제하기
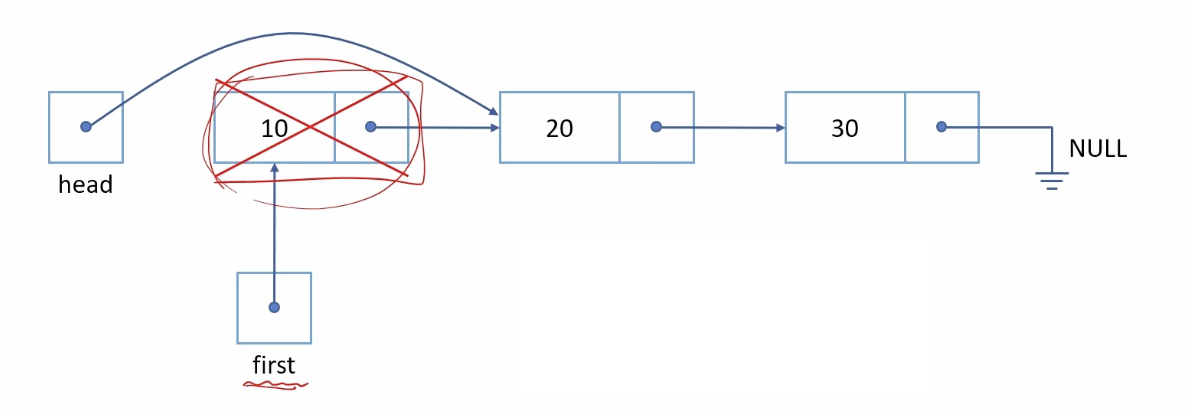
void pop_front()
{
if(head == NULL)
return;
Node* first = head;
head = head->next;
delete first;
}head가 NULL를 가리키면 종료를 시킨다.
head가 가리키고 있는 걸 first로 연결시키고, head는 head의 다음 값이 가리고 있던 next를 가리킨다.
그리고 first를 삭제시킨다.
∙ 연결 리스트 전체 데이터 출력하기
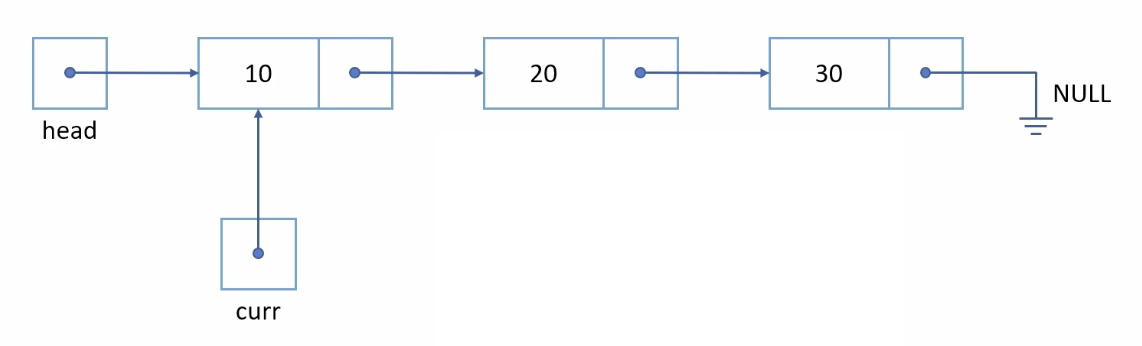
void print_all()
{
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL){
cout << curr -> data <<", ";
curr = curr -> next;
}
}curr가 가리키는 data값을 출력시키고, curr를 data가 가리키고 있던 next를 가리켜준다.(curr가 NULL이 아닐 때까지)
∙ 연결 리스트가 비어 있는지 확인
bool empty()
{
return head == NULL;
}
∙ 연결 리스트 예제 코드
#include <iostream>
struct Node
{
int data;
Node* next;
};
class LinkedList
{
private:
Node* head;
public:
LinkedList() : head(NULL) {};
~LinkedList()
{
while (!empty()) {
pop_front();
}
}
void push_front(int val)
{
Node* new_node = new Node {val, head};
if (head != NULL)
new_node->next = head;
head = new_node;
}
void pop_front()
{
if (head == NULL)
return;
Node* first = head;
head = head->next;
delete first;
}
bool empty() const
{
return head == NULL;
}
void print_all() const
{
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
std::cout << curr->data << ", ";
curr = curr->next;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
};
int main()
{
LinkedList ll;
ll.push_front(10);
ll.push_front(20);
ll.push_front(30);
ll.print_all();
ll.pop_front();
ll.print_all();
ll.push_front(40);
ll.print_all();
}

∙ 연결 리스트의 장점
- 임의의 위치에 원소의 삽입 & 삭제가 효율적
- 크기 제한이 없음
∙ 연결 리스트의 단점
- 임의의 원소 접근이 비효율적
- 링크를 위한 여분의 공간 사용
- 구현이 복잡
• 프로그래머스 실습
#include <string>
#include <vector>
//sort 함수를 사용하기 위한 include
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int solution(vector<int> array) {
int answer = 0;
//sort 사용하기 위해 시작부터 끝 배열을 적어줘야함
sort(array.begin(),array.end());
//중앙값을 구하기 위해 정렬된 배열중에 가운데 구함
answer = array[array.size()/2];
return answer;
}

